Table Of Content
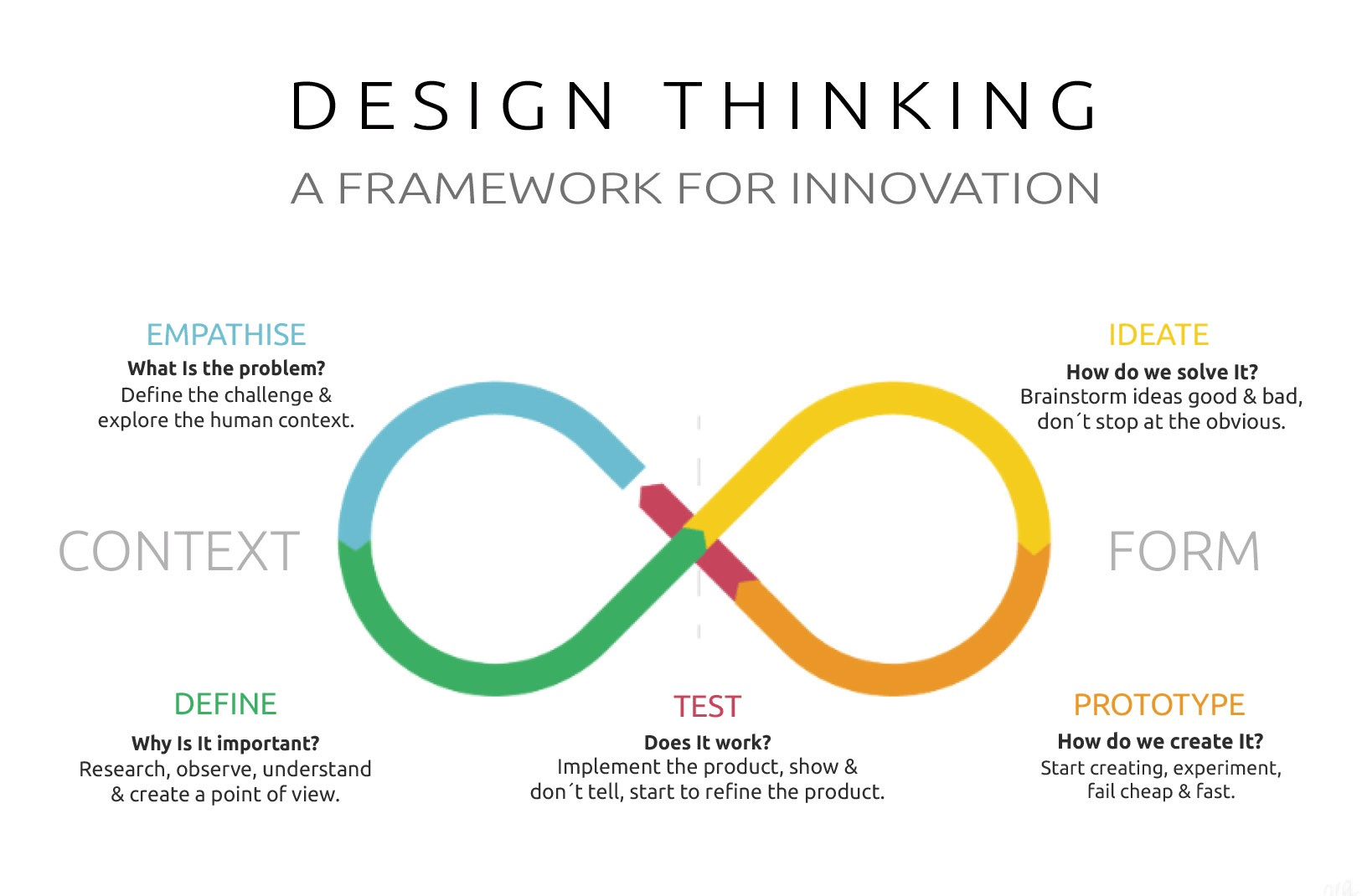
When you know how to apply the five stages of design thinking you will be impowered because you can apply the methodology to solve complex problems that occur in our companies, our countries, and across the world. The testing stage is normally one of the last stages of the design thinking process. After you’ve developed a concept or prototype, you need to test it in the real-world to understand its viability and usability.
The Design-Thinking method for stimulating knowledge transfer in organisations - Universiteit Leiden
The Design-Thinking method for stimulating knowledge transfer in organisations.
Posted: Tue, 20 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Want to learn more about design thinking?
Design Thinking is especially useful when it comes to solving “wicked problems”. The term “wicked problem” was coined by design theorist Horst Rittel in the 1970s to describe particularly tricky problems that are highly ambiguous in nature. Now we know more about how Design Thinking works, let’s consider why it matters. There are many benefits of using a Design Thinking approach—be it in a business, educational, personal or social context. Prototypes are key to striking balance between customer and client needs, Schrage said, but not in the way you might expect.
common challenges and pitfalls in design thinking
He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries. That, in turn, helped them create better meals (which were also drastically changed), yielding happier, better nourished customers. A tool like Hotjar lets you observe user behavior in your product and ask the right questions at the right time.
References & Where to Learn More
Once you’ve formulated the problem into words, you can start to come up with solutions and ideas — which brings us onto stage three. The first stage of the process is spent getting to know the user and understanding their wants, needs and objectives. Design thinking is both an ideology and a process, concerned with solving complex problems in a highly user-centric way. Design thinking provides a structured process that helps innovators break free of counterproductive tendencies that thwart innovation. Like TQM, it is a social technology that blends practical tools with insights into human nature. ” It is an attempt to empathize with the needs and desires of current or potential users through in-depth interviews and close observation.
Prototype and test. Repeat.
In this phase you begin to weigh the impact vs. feasibility of your ideas through feedback on your prototypes. In the define phase, use the data gathered in the empathize phase to glean insights. Organize all your observations and draw parallels across your users’ current experiences. Repeating this loop of prototyping, testing, and gathering user feedback is crucial for making sure the design is right — that is, it works for customers, you can build it, and you can support it. The first step in design thinking is to understand the problem you are trying to solve before searching for solutions.
As we advance into a future where projects become increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to integrate and apply these models alongside established IT methodologies will be a defining skill for IT professionals. This systemic integration not only enhances their capacity to address current challenges but also positions them to lead the way in shaping the digital landscapes of tomorrow. Design thinking is often referred to as outside-the-box thinking, as designers attempt to develop new ways of thinking that do not abide by the dominant or more common problem-solving methods—just like artists do. Design thinking is essentially a problem-solving approach that has the intention to improve products.
Design thinking examples: What it looks like in practice
The design sprint is Google Ventures’ version of the design thinking process, structured to fit the design process in 1 week. The methodology emphasizes collaboration and a multidisciplinary approach throughout each phase to ensure solutions are innovative and deeply rooted in real human needs and contexts. Global design leaders and consultants have interpreted the abstract design process in different ways and have proposed other frameworks of design thinking.
In business
The end result was Society of Grownups, a suite of digital tools that help to educate young people to make smart financial choices. Design thinking is increasingly being integrated into business as a way to foster innovation and teamwork. Perhaps you want to focus on the collaborative nature of design thinking, in which case you might hold ideation sessions with representatives from a diverse variety of teams. If you notice that marketing and design constantly struggle to see eye-to-eye, for example, a few design thinking-style brainstorming sessions might help to get everybody on the same page. Although these steps appear to be sequential, it’s important to point out that design thinking doesn’t follow a strictly linear process. At each stage in the process, you’re likely to make new discoveries that require you to go back and repeat a previous step.
Make product decisions based on what your users need

Deciding on the strategy—how the project will achieve its goals—ties into lean thinking, which emphasizes value streams and waste elimination. For IT developers, understanding the chosen strategy informs the selection of technologies, architectural patterns and development practices that align with project goals. This strategic alignment ensures that resources are optimized and efforts are directed toward activities that directly contribute to the project's objectives. Identifying primary choices involves setting clear, measurable goals, a principle that resonates with the outcome-focused nature of agile methodologies. For developers, defining these outcomes provides a clear direction for the project, facilitating prioritization and helping to maintain focus on delivering value to the end-users.
It is applied in user experience (UX) design and user interface (UI) design to create products specifically with user needs in mind, and focuses on being solution-based rather than being problem-based. The first step in finding success with design thinking is to foster a culture of human-centered design within your team. This is because design thinking focuses so heavily on the users and customers — the people using your product or service. Design thinking gives teams a new way to approach their projects and overcome some of those well-known challenges. It can help teams understand their users' needs and challenges, then apply those learnings to solve problems in a creative, innovative way.
It’s where your product, design, or development teams evaluate the creative solutions they’ve come up with, to see how real users interact with them. During the third stage of the design thinking process, designers are ready to generate ideas. You’ve grown to understand your users and their needs in the Empathize stage, and you’ve analyzed your observations in the Define stage to create a user centric problem statement. With this solid background, you and your team members can start to look at the problem from different perspectives and ideate innovative solutions to your problem statement. Design thinking refers to procedures applied in the design process that help make decisions and address roadblocks in a user-centric manner.
Wicked problems demand teams to think outside the box, take action immediately, and constantly iterate—all hallmarks of design thinking. In the first study we investigated how UX and design professionals define design thinking. As you walk around the world, you should try to look for the design stories that are all around you. Say to yourself “that’s an example of great design” or “that's an example of really bad design” and try to figure out the reasons why. Together, Design Thinking, lean, and agile cut out unnecessary processes and documentation, leveraging the contributions of all key stakeholders for continuous delivery and improvement.
Depending on time constraints, you will gather a substantial amount of information to use during the next stage. The main aim of the Empathize stage is to develop the best possible understanding of your users, their needs and the problems that underlie the development of the product or service you want to create. Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams develop new ideas. While design thinking and agile teams share principles like iteration, user focus, and collaboration, they are neither interchangeable nor mutually exclusive.

No comments:
Post a Comment